Important note: As we approach the period spanning the end of May and beginning of June when Bilderberg meetings are ordinarily scheduled, it should be observed that the home page of the official Bilderberg website currently declares in bold capitals:
THE MEETING 2020 IS POSTPONED.
It does not say for how long.
*
Just because you’re paranoid doesn’t mean they aren’t after you
— Joseph Heller 1
This is the fourth of a sequence of articles based around the ‘key topics’ at last year’s Bilderberg conference discussed here in relation to the prevailing political agenda and placed within the immediate historical context.
This piece focuses on issues relating to the weaponsation of social media and cyber threats:

A schematically enhanced version of last year’s ‘key topics’
*
JTRIG was in the business of discrediting companies, by passing “confidential information to the press through blogs etc.”, and by posting negative information on internet forums. They could change someone’s social media photos (“can take ‘paranoia’ to a whole new level”, a slide read.) They could use masquerade-type techniques – that is: placing “secret” information on a compromised computer. They could bombard someone’s phone with text messages or calls.
JTRIG also boasted an arsenal of 200 info-weapons, ranging from in-development to fully operational. A tool dubbed “Badger” allowed the mass delivery of email. Another, called “Burlesque”, spoofed SMS messages. “Clean Sweep” would impersonate Facebook wall posts for individuals or entire countries. “Gateway” gave the ability to “artificially increase traffic to a website”. “Underpass” was a way to change the outcome of online polls.
The Joint Threat Research Intelligence Group (JTRIG) is a unit attached to Britain’s GCHQ. The summary above is based on a slides leaked by Edward Snowden. It outlines the sorts of disinformation tactics being deployed against targets across the world (including domestic ones) as far back as 2013. Of course, this is long before mainstream reports of Russian troll farms and the consequent calls for active internet censorship to save us from the ever-present threat of “fake news”.
Entitled “Inside the British Army’s secret information warfare machine”, the same Wired report devotes its main attention to the slightly better known UK disinfo operation, the 77th Brigade, that was founded officially in January 2015, although its establishment had in actuality involved the rebranding of a different agency formerly known as the “Security Assistance Group” 2:
Walking through the headquarters of the 77th, the strange new reality of warfare was on display. We’ve all heard a lot about “cyberwarfare” – about how states could attack their enemies through computer networks, damaging their infrastructure or stealing their secrets. But that wasn’t what was going on here. Emerging here in the 77th Brigade was a warfare of storyboards and narratives, videos and social media. An engagement now doesn’t just happen on the battlefield, but also in the media and online. A victory is won as much in the eyes of the watching public as between opposing armies on the battlefield. Warfare in the information age is a warfare over information itself.
A few paragraphs down, we also learn that:
Inside the base of the 77th, everything was in motion. Flooring was being laid, work units installed; desks – empty of possessions – formed neat lines in offices still covered in plastic, tape and sawdust. The unit was formed in a hurry in 2015 from various older parts of the British Army – a Media Operations Group, a Military Stabilisation Support Group, a Psychological Operations Group. It has been rapidly expanding ever since.
In 2014, a year before the 77th was established, a memo entitled “Warfare in the Information Age” flashed across the British military. “We are now in the foothills of the Information Age” the memo announced. It argued that the British Army needed to fight a new kind of war, one that “will have information at its core”. The Army needed to be out on social media, on the internet, and in the press, engaged, as the memo put it, “in the reciprocal, real-time business of being first with the truth, countering the narratives of others, and if necessary manipulating the opinion of thousands concurrently in support of combat operations.” 3
Click here to read the full article in Wired magazine.
In March 2018, James Corbett foreshadowed the Bilderberg group with a broadcast of his own show entitled “The Weaponization of Social Media”:
*
New America
The New America Foundation has received more than $21 million from Google; its parent company’s executive chairman, Eric Schmidt; and his family’s foundation since the think tank’s founding in 1999. That money helped to establish New America as an elite voice in policy debates on the American left and helped Google shape those debates.
According to a New York Times article from August 2017 entitled “Google Critic Ousted From Think Tank Funded by the Tech Giant”. The critic in question was a scholar working for New America called Barry Lynn who posted a statement on the think tank’s website applauding European Commissioner for Competition Margrethe Vestager for levying a fine of 2.4 billion euros against Google for breaching EU antitrust laws.
The same NYT report continues:
“New America financial supporters have no influence or control over the research design, methodology, analysis or findings of New America research projects, nor do they have influence or control over the content of educational programs and communications efforts,” [New America’s executive vice president] Ms. [Tyra] Mariani said. She added that Mr. Lynn’s statement praising the European Union’s sanctions against Google had been temporarily removed from New America’s website because of “an unintentional internal issue” unrelated to Google or Mr. [Eric] Schmidt.
Ms. Mariani and Ms. [Riva] Sciuto [a Google spokeswoman] said Google is continuing to fund New America.
Hours after this article was published online Wednesday morning, Ms. [Anne-Marie] Slaughter announced that the think tank had fired Mr. Lynn on Wednesday for “his repeated refusal to adhere to New America’s standards of openness and institutional collegiality.”
Ms. Slaughter also wrote on Twitter that the article was “false,” but was unable to cite any errors. New America would not make Ms. Slaughter available for an interview. 4
So what? Why am I writing about this hand-in-glove relationship between tech giant Google and the Executive Chairman of its parent company Alphabet Inc., Eric Schmidt, with a think tank formerly known as New America Foundation but since renamed simply New America? The short answer is one man: Peter Warren Singer.
A strategist for America Foundation, P.W. Singer specialises in 21st century warfare. In a few years he has published nothing short of a small library of books on related topics ranging from the post-9/11 rise of the mercenary armies, child soldiers, military robotics, cybersecurity and cyberwarfare. Amongst his most recent publications, LikeWar: The Weaponization of Social Media (2018) is already regarded as a seminal work.
If “CyberWar” is about hacking networks, “LikeWar” is about hacking the people on the networks, driving ideas viral through a mix of “likes” and lies. And in these battles for virality, which can generate real world power, generating a sense of authenticity has become an important milestone for any online operation, be it selling an album, a political campaign, or an information warfare operation designed to cause your enemies army to run away (as in the #AllEyesOnISIS operation). 5
From an article by P.W. Singer and co-author Emerson Brooking entitled “What Taylor Swift Teaches Us About Online War” published around the time of the book launch by Defense One in October 2018.
Funnily enough, and only a few months later, Singer was invited to the 2019 Bilderberg gathering in Montreux, when one of the key topics happened to be “The weaponisation of social media”.
I wonder whether he contributed to the discussion at all, and found the time to chew the cud with Bilderberg warhorse and his New America Foundation benefactor and Chairman Emeritus, Eric Schmidt.
*
(Everything is) LikeWar
The pattern of military hardware silhouettes above welcomes visitors to P.W. Singer’s official website. To judge from his CV, he very probably has the same wallpaper up in his bedroom.
In a recent interview he told Lauren Hepler:
Social media is not just a communication space and a marketplace. It’s also a battle space. You have sides that go back and forth. They use tactics and strategies to achieve their goals. We’ve seen its weaponization to target elections, to target military units. We’ve seen it used to target corporations to try to sabotage their share price, to harm the rollout of a new product. We’ve also seen it have a real and very sad impact on public health.
This is now a matter of life and death. The deliberate spread of misinformation on coronavirus didn’t just shape a laggard Trump administration response, but also shaped individual-level decisions that were irresponsible and dangerous. It cost lives.
Singer calls a response at all levels: individual, governmental and, importantly, corporate:
Then we had coronavirus breakout, and all of them [‘the platform companies’] again implemented things [forms of censorship] that were unthinkable, impossible for them to do just a few months earlier. They should be applauded for doing it, but as they take on more and more of a political role, they are forced to play politics. For example, when someone posts information about a medical treatment that is not effective and maybe even dangerous, they knocked offline certain individuals for doing that, but not others because they’re a little bit too prominent, and if we do, then it will look like we’re playing politics.
Singer’s view is that playing politics is fine, indeed something the tech giants “should be applauded for doing”, however in western democracies, maintaining appearances is of the utmost importance. He continues:
I’m incredibly empathetic toward these companies, because they’re being forced to play this role in the U.S. essentially because we have not updated our election rules. In other nations, the companies have more guidance.
Incredibly empathetic… well, you’re hardly going to bite the hand that feeds you! But what is Singer’s role here? As a former Senior Fellow at the Brookings Institute and current Strategist for New America, whose major donors besides Eric and Wendy Schmidt also include the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and the US State Department, Singer is clearly in the business of shaping US government policy on behalf of corporate interests. In this instance, enjoining the government to issue “guidance” on censorship such that the tech giants are then able to distance themselves from policies deliberately brought in to marginalise dissident voices.
A Washington Post article published in late 2016 entitled “Why Facebook and Google are struggling to purge fake news” made the matter plain:
Facebook, Google and other Web companies have sought to walk a fine line: They don’t want to get into the practice of hiring human editors, which they believe would make them vulnerable to criticisms of partisan bias and stray from their core business of building software. Yet outsiders, as well as some within Silicon Valley, are increasingly clamoring for technology giants to take a more active role in policing the spread of deceptive information.
“It is very difficult for Facebook to say they are not a gatekeeper when they drive such an enormous share of the attention of most news consumers across the world,” said Joshua Benton, director of the Nieman Journalism Lab at Harvard University. “They need to figure out some editorial mechanism; with their scale comes responsibility.” 6
Singer admits:
A few weeks ago, there was a blast of kind-of-weird content moderation happening. It was because the platform companies had to send many of their people home, and they were using more and more AI that was understandably squirrelly. People were looking for conspiracy, when it was just AI doing its thing. 7
As an esteemed expert in his field Singer must know very well, of course, that this excuse of ‘squirrelly AI’ is actually a red herring. After all, the internet clampdown and “kind-of-weird content moderation” didn’t spring forth inadvertently on the back of the coronavirus lockdown a few weeks ago, but has been incrementally ratcheted up even before the first stirrings of the “Russiagate” hoax four years ago. As I pointed out in an earlier piece, fears of the fabled internet “kill switch” are a distraction, as the volume of dissident voices is being steadily turned down and the internet is slowly shut down by stealth.
*
Project Birmingham: Alabama’s ‘fake news’ false flag
At least 1,100 Russian-language accounts followed Republican U.S. Senate nominee Roy Moore’s Twitter account over the past few days. Moore’s team says they want to know why.
So begins an article in local newspaper the Montgomery Advertiser entitled “Russian invasion? Roy Moore sees spike in Twitter followers from land of Putin”
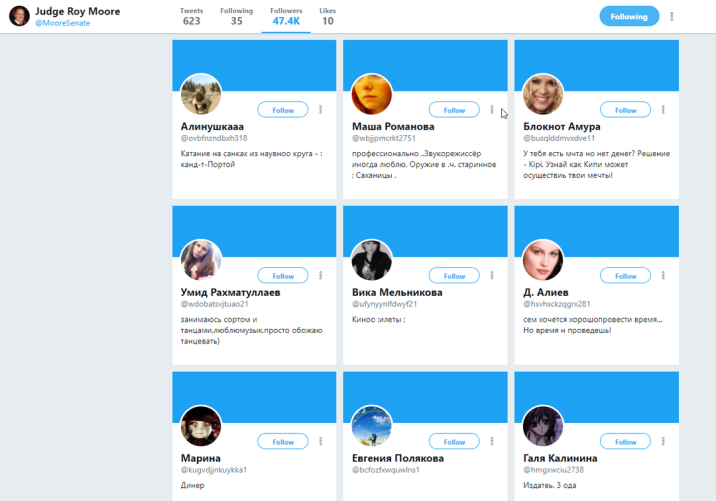
Caption retained:
A screen cap of Republican U.S. Senate nominee Roy Moore’s Twitter followers on Monday, Oct. 16, 2017. Moore’s campaign accounts was followed by thousands of Cyrillic-language accounts in the days prior. The Moore campaign says they have asked Twitter to investigate. (Photo: Twitter)
Beneath a composite image showing just a few examples of this huge army of Russian Twitter bots (see above), the same report into the stormy Alabama 2017 senate race between Republican Roy Moore and rival Democrat Doug Jones continues:
“We had absolutely nothing to do with this,” said Drew Messer, a spokesman for the campaign, on Monday. “We’ve never purchased followers or dummy ads on Twitter. We’ve asked Twitter to look into this.”
The increase helped push Moore’s following on Twitter from about 27,000 accounts on Friday to over 47,000, ahead of Democratic nominee Doug Jones, who has about 39,000 followers on Twitter.
Adding:
The Jones campaign Monday evening said Moore was “embarrassing the people of Alabama with another disgusting and pathetic lie.”
“Maybe Moore should check with Vladimir Putin, who shares his views on depriving people of their civil rights,” the statement said. 8
Although Moore had been leading in the polls by six to eight points, it was finally Democrat Jones who went on to win the election. So had the disclosure of Russian influence during the campaign finally affected the result? Very possibly, although in the fullness of time something more extraordinary was revealed by an internal report. Those thousands of bots meddling in the campaign had not been Russian at all and had no connection whatsoever to Putin. Instead they were part of “an experiment”:
One participant in the Alabama project [aka ‘Project Birmingham’], Jonathon Morgan, is the chief executive of New Knowledge, a small cyber security firm that wrote a scathing account of Russia’s social media operations in the 2016 election that was released this week by the Senate Intelligence Committee. […]
The project’s operators created a Facebook page on which they posed as conservative Alabamians, using it to try to divide Republicans and even to endorse a write-in candidate to draw votes from Mr. Moore. It involved a scheme to link the Moore campaign to thousands of Russian accounts that suddenly began following the Republican candidate on Twitter, a development that drew national media attention.
“We orchestrated an elaborate ‘false flag’ operation that planted the idea that the Moore campaign was amplified on social media by a Russian botnet,” the report says.
The same piece includes a number of statements for Morgan, including this explanation:
Mr. Morgan said in an interview that the Russian botnet ruse “does not ring a bell,” adding that others had worked on the effort and had written the report. He said he saw the project as “a small experiment” designed to explore how certain online tactics worked, not to affect the election.
“The research project was intended to help us understand how these kind of campaigns operated,” said Mr. Morgan. “We thought it was useful to work in the context of a real election but design it to have almost no impact.” 9
Click here to read the full New York Times article published in December 2018 entitled “Secret Experiment in Alabama Senate Race Imitated Russian Tactics”.
Jonathan Morgan’s New Knowledge is a Texas-based cybersecurity firm, and behind it we find far larger concerns in the shape of American Engagement Technologies (AET) and for-profit investment management firm Investing In US. This is a trail I shall return to below.
However, it turns out that this phoney Russiagate operation was only part of the information warfare strategy. A separate effort had involved an elaborate fake campaign intended to convince voters of Republican candidate Moore’s supposed plans to reintroduce alcohol prohibition:
The “Dry Alabama” Facebook page, illustrated with stark images of car wrecks and videos of families ruined by drink, had a blunt message: Alcohol is the devil’s work, and the state should ban it entirely.
Along with a companion Twitter feed, the Facebook page appeared to be the work of Baptist teetotalers who supported the Republican, Roy S. Moore, in the 2017 Alabama Senate race. “Pray for Roy Moore,” one tweet exhorted.
In fact, the Dry Alabama campaign, not previously reported, was the stealth creation of progressive Democrats who were out to defeat Mr. Moore — the second such secret effort to be unmasked.
So who was behind these disinformation campaigns? The same NYT piece continues:
The revelations about the first project, run in part by a cybersecurity company called New Knowledge, led Facebook to shut down five accounts that it said had violated its rules, and prompted Senator [Doug] Jones to call for a federal investigation. There is no evidence that Jones encouraged or knew of either of the deceptive social media projects. His spokeswoman, Heather Fluit, said his legal advisers were preparing to file a formal complaint with the Federal Election Commission. […]
The first of the Alabama efforts was funded by Reid Hoffman, the billionaire co-founder of LinkedIn, who apologized and said he had been unaware of the project and did not approve of the underhanded methods. The second was funded by two Virginia donors who wanted to defeat Mr. Moore — a former judge accused of pursuing sexual relationships with underage girls — according to a participant who would speak about the secret project only on the condition of anonymity and who declined to name the funders.
The two projects each received $100,000, funneled in both cases through the same organization: Investing in Us, which finances political operations in support of progressive causes. Dmitri Mehlhorn, the group’s managing partner, declined to comment on whether he approved of the tactics he had helped pay for. 10
For the record, Investing in US was co-founded by Reid Hoffman and Dmitri Mehlhorn, a former senior fellow at the Progressive Policy Institute.
Click here to read the full NYT report entitled “Democrats Faked Online Push to Outlaw Alcohol in Alabama Race”.
*
Pulling the strings back at Bilderberg
Reid Hoffman may be a name that is unfamiliar to you, even though he was co-founder and executive chairman of LinkedIn. As we learn from a NYT puff piece from 2011, after a shaky start, Hoffman was fortunate enough to have some well-connected associates:
In 1985, Mr. Hoffman enrolled at Stanford, where he majored in symbolic systems, the study of the relationship between computing and human intelligence. He soon befriended a fellow student, Peter Thiel, who would go on to found PayPal.
When his own social media start-up SocialNet flopped, Hoffman was invited to rejoin his old pal as Thiel was setting up PayPal:
As an executive vice president, it was up to Mr. Hoffman to manage external relations. “He was the firefighter in chief at PayPal,” Mr. Thiel says. “Though that diminishes his role because there were many, many fires.” 11
Click here to read the full NYT article entitled “A King of Connections Is Tech’s Go-To Guy”
Peter Thiel and Reid Hoffman today sit at the high table as Bilderberg regulars alongside Eric Schmidt – the trio of techies have each attended every conference during the last four years: Thiel going under the title President of Thiel Capital; Hoffman more self-effacingly as a ‘Partner’ at Greylock Partners; and Schmidt, evidently the most modest of the three, declaring himself a mere ‘Technical Advisor’ to Alphabet Inc.
*
Please note: I started constructing this article as part of a larger review (that was subsequently broken down into this series of smaller pieces) many months prior to the current coronavirus crisis and lockdown.
1 Though it is not referenced by Wikiquote, there are a wide variety of sources including articles published by the Guardian and The Atlantic magazine that have attributed Joseph Heller’s novel Catch-22 as the original source of this quote. Variations of the same quote are also misattributed to American singer, songwriter, and musician, best known as the guitarist and frontman of the rock band Nirvana, Kurt Cobain.
2 https://www.parliament.uk/business/publications/written-questions-answers-statements/written-question/Commons/2015-02-24/225283/
3 From an article entitled “Inside the British Army’s secret information warfare machine” written by Carl Miller, published in Wired on November 14, 2018. https://www.wired.co.uk/article/inside-the-77th-brigade-britains-information-warfare-military
4 From an article entitled “Google Critic Ousted From Think Tank Funded by the Tech Giant” written by Kenneth P. Vogel, published in The New York Times on August 30, 2017. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/08/30/us/politics/eric-schmidt-google-new-america.html?_r=0
5 From an article entitled “What Taylor Swift Teaches Us About Online War” written by Peter W. Singer & Emerson T. Brooking, published in Defense One on October 2, 2018. https://www.defenseone.com/ideas/2018/10/what-taylor-swift-teaches-us-about-online-war/151634/?oref=d-river
6 From an article entitled “Why Facebook and Google are struggling to purge fake news” written by Elizabeth Dwoskin, Caitlin Dewey & Craig Timberg, published in the Washington Post on November 15, 2016. https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/economy/why-facebook-and-google-are-struggling-to-purge-fake-news/2016/11/15/85022897-f765-422e-9f53-c720d1f20071_story.html
7 From an article entitled “A futurist on Covid-19 and business: Pandora’s box is now open” written by Lauren Hepler, published in Protocol on April 19, 2020. https://www.protocol.com/cyberwar-expert-pw-singer-coronavirus
8 From an article entitled “Russian invasion? Roy Moore sees spike in Twitter followers from land of Putin” written by Brian Lyman, originally published in the Montgomery Advertiser on October 16, 2017 (updated December 12, 2019) https://eu.montgomeryadvertiser.com/story/news/politics/southunionstreet/2017/10/16/roy-moores-twitter-account-gets-influx-russian-language-followers/768758001/
9 From an article entitled “Secret Experiment in Alabama Senate Race Imitated Russian Tactics” written by Scott Shane & Alan Blinder, published in The New York Times on December 19, 2018. https://www.nytimes.com/2018/12/19/us/alabama-senate-roy-jones-russia.html
10 From an article entitled “Democrats Faked Online Push to Outlaw Alcohol in Alabama Race” written by Scott Shane & Alan Blinder, published in The New York Times on January 7, 2019. https://www.nytimes.com/2019/01/07/us/politics/alabama-senate-facebook-roy-moore.html?action=click&module=Top%20Stories&pgtype=Homepage
11 From an article entitled “A King of Connections Is Tech’s Go-To Guy” written by Evelyn M. Rusli, published in The New York Times on November 5, 2011. https://www.nytimes.com/2011/11/06/business/reid-hoffman-of-linkedin-has-become-the-go-to-guy-of-tech.html?pagewanted=all




Pingback: JTRIG – „Soziale“ Medien als Waffe – Blauer Bote Magazin – Wissenschaft statt Propaganda